Embracing the Future: Unpacking the New IEC 63452 Railway Cybersecurity Standard
Published on:
The introduction of the IEC 63452 standard next year will represent a crucial update in the realm of railway systems cybersecurity. This standard will replace the current Technical Specification, TS 50701, enhancing and expanding the framework to better address today’s cybersecurity challenges within the railway industry.
Detailed Cybersecurity Framework
IEC 63452 introduces a more specific cybersecurity framework designed for railway applications. It emphasises continuous monitoring and cybersecurity assurance, allowing railway operators to respond more effectively to changing threats. The standard organises vulnerability management in a structured way, ensuring timely identification and mitigation of security vulnerabilities to protect critical infrastructure.

Enhanced Risk Management
IEC 63452 offers detailed methodologies for risk assessment, advancing beyond the broader guidelines of TS 50701. It includes classification of different areas within the railway system based on their security needs, facilitating targeted and efficient security measures.
Integration of Safety and Security
IEC 63452 integrates the management of safety and security considerations, encouraging a combined approach to engineering these aspects to improve overall system integrity and reliability. The standard promotes measurable security measures providing a framework to evaluate security effectiveness. In continuation of the approach and improving it.

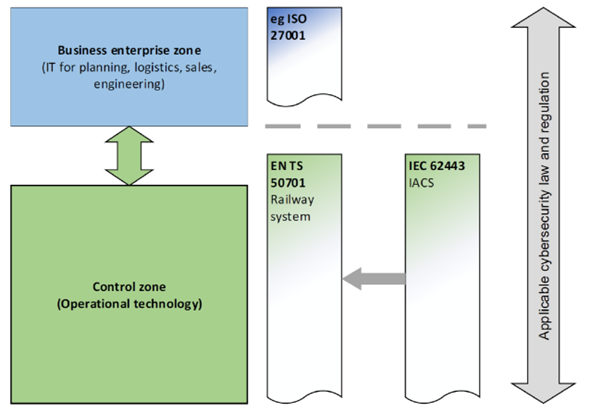
The standard provides a comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity within railway systems, adhering to the guidelines of IEC TC 9 and applicable across all relevant sectors within the railway industry.
It integrates the requirements from the IEC 62443 series, which are specifically designed for cybersecurity, and adapts these for the railway application domain. This includes a detailed application of cybersecurity standards and instructions on interfacing these standards with the general reliability, availability, maintainability, and safety (RAMS) lifecycle as outlined in the IEC 62278 series.
The standard ensures synchronization among various stakeholders by defining their responsibilities and presenting the security assumptions clearly. It also outlines how these cybersecurity protocols can be applied to other lifecycle processes.
Compliance with IEC 62443-2-1:2010 is maintained, providing security models, concepts, and a risk assessment process specifically tailored for the railway sector. This approach helps identify and manage residual risks associated with security threats to a level that is acceptable for railway operators and infrastructure managers.
The primary goal of the standard is to offer support and guidance for protecting critical aspects of railway Systems under Consideration (SuC) such as safety, operations, financial interests, reputation, regulatory compliance, and social stakes against cyber-attacks and the unintended consequences of configuration or maintenance activities.
Additionally, the standard provides guidance on cybersecurity assurance during the build phase of SuCs and offers recommendations for security management during the operational and maintenance phases.
It is important to note that while the standard provides a robust framework for cybersecurity and its integration with safety, it does not set forth any specific safety requirements or constraints on safety cases for railway systems. Instead, it guides on how cybersecurity measures relate to safety protocols.
Lifecycle Management
The standard provides comprehensive guidelines that span the entire lifecycle of railway systems, from installation to decommissioning. This approach ensures that cybersecurity is an integral part of every stage in a system’s lifecycle, enhancing the long-term sustainability and security of railway operations.
Future Implications
The adoption of IEC 63452 is a useful step towards addressing the complex cybersecurity issues currently facing the railway industry. By establishing a robust framework that incorporates risk management, and integrates safety and security throughout the system’s lifecycle, IEC 63452 aims to set a new standard for railway cybersecurity globally.